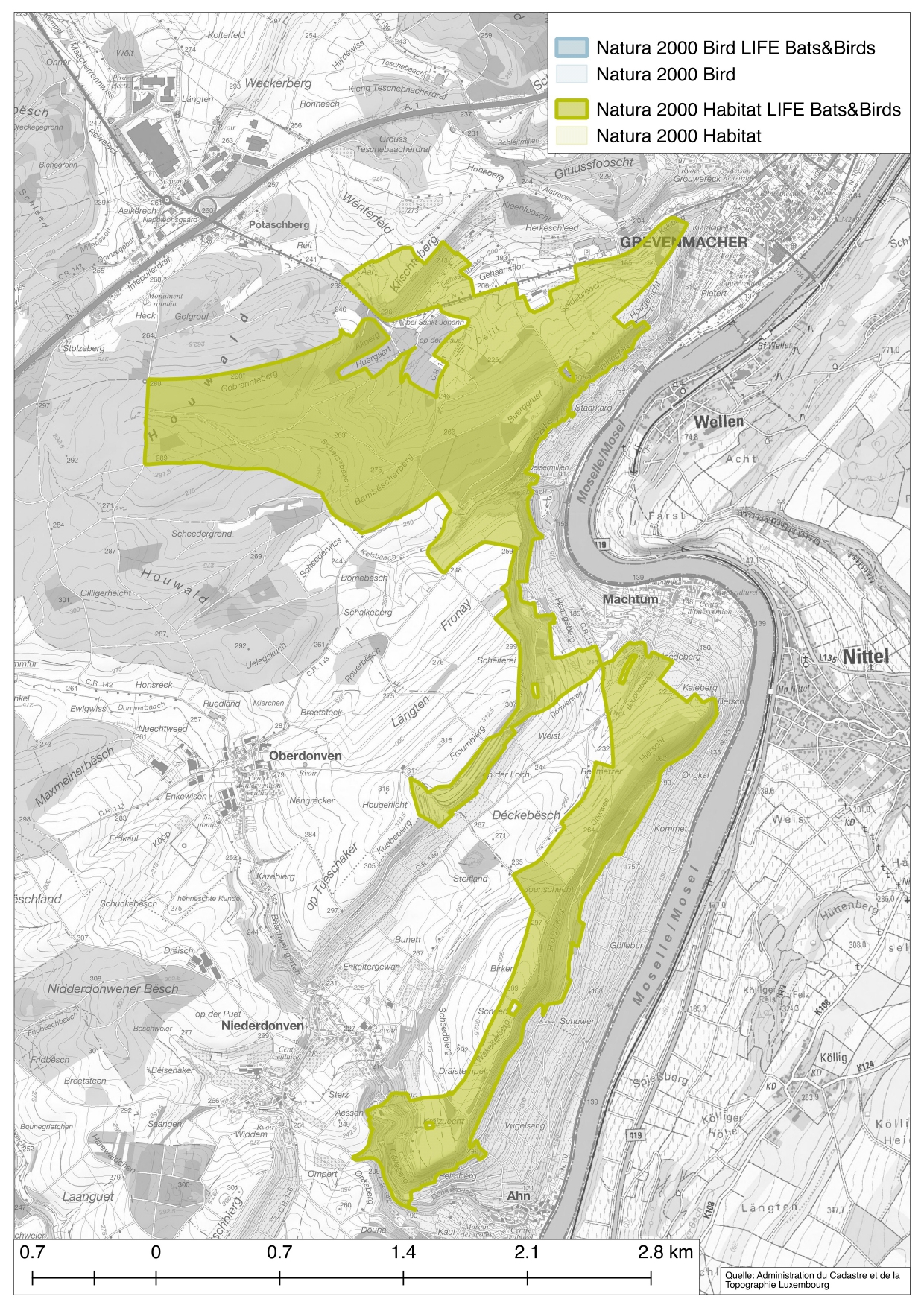
The Natura 2000 Habitat Conservation Area Machtum-Pellembierg / Froumbierg / Greivenmaacherbierg stretches along the narrow Moselle valley from Ahn in the southeast to Grevenmacher in the northeast. Geologically, the area is characterised by limestone-rich sediments with formations of Keuper and Muschelkalk. While the ground on the plateaus is dominated by marls, dolomitic rocks of Muschelkalk are found below. These dolomites, some of which are massive, form imposing rock edges in the landscape, which are particularly visible in the Moselle valley between Machtum and Grevenmacher. The faults running parallel to the Moselle partially shape the appearance of the landscape strongly. The shifting of the rock has lifted the older, lower-lying shell limestone layers respectively, creating striking escarpments. The soils on the plateau consist mainly of loamy para-brown soils to pelosols. On the slopes, the soils are shallower and dominated by stone and clay rich brown earths. Due to the lime-rich subsoil, the slopes were formerly used as vineyard terraces. Afterwards, they were partly used for fruit growing as well as for grazing or mowing, resulting in semi-dry grasslands. However, as these areas are costly to cultivate and the yield is rather low, many uses have been abandoned and the terraces are now largely overgrown with bushes. The undulating valleys, on the other hand, are easier to machine and are therefore intensively used for agriculture. The most important watercourses in the area are the Donwerbaach, Kelsbaach and Gehaansbaach, which all flow into the Moselle. These streams show a very different character during drought and heavy rainfall. In summer they partially dry up, whereas they can turn into torrents during heavy rain. A special feature of this area is the natural, albeit small-scale, occurrence of boxwood formations in the area of the Pellembierg. The viticultural climate in this part of the country favours these occurrences. The limestone rock formations of this area, with their caves and galleries, provide an ideal habitat for bats. Due to the diverse structures of the landscape, they find roosts for every situation, i.e. nursery roosts, male roosts and mating roosts, as well as hibernation roosts. The area consists of about one third open land and more than half forest habitats. More than one third of the Natura 2000 site Machtum-Pellembierg / Froumbierg / Greivenmaacherbierg are habitats designated under Annex I of the Habitats Directive. Various forest communities and lowland meadows (6510) dominate in the open countryside. A total of 11 different habitats were recorded in the area. According to the SDF (Standard Data Form), 5 bat species, including both target species, and one insect species occur in the project area among the animal species protected under Annex II of the Habitats Directive. In addition, another 6 plant species, 2 insect species and 3 bat species are important in the area due to their rarity and/or speciality. Among the 7 species protected under Annex I of the Birds Directive in the area according to the SDF, three of the four target species are also present.
Machtum